Vivienne Prince

Thanks for dropping by my page!
I'm currently a Masters of Data Science student graduating in 2022.
I really enjoy learning new tools, exploring data to help solve problems, and helping others understand ideas and data.
Steepest Descent Optimization with Optimal Step Size (Wolfe) and Newton’s Method Demo in Python
November 2020 – Me
Overview:
I l0ve math, and was really excited to learn about optimization algorithms.
This google colab sheet demonstrates steepest decent algorithms using numeric approximation.
Tools:
Numpy: matrix operations
Matplotlib: viz
Language used: Python
See my demo here. :-D
Here’s a preview:
for function f(x,y) = (x+1)^2 + 8y^2 - 3x - y + 1
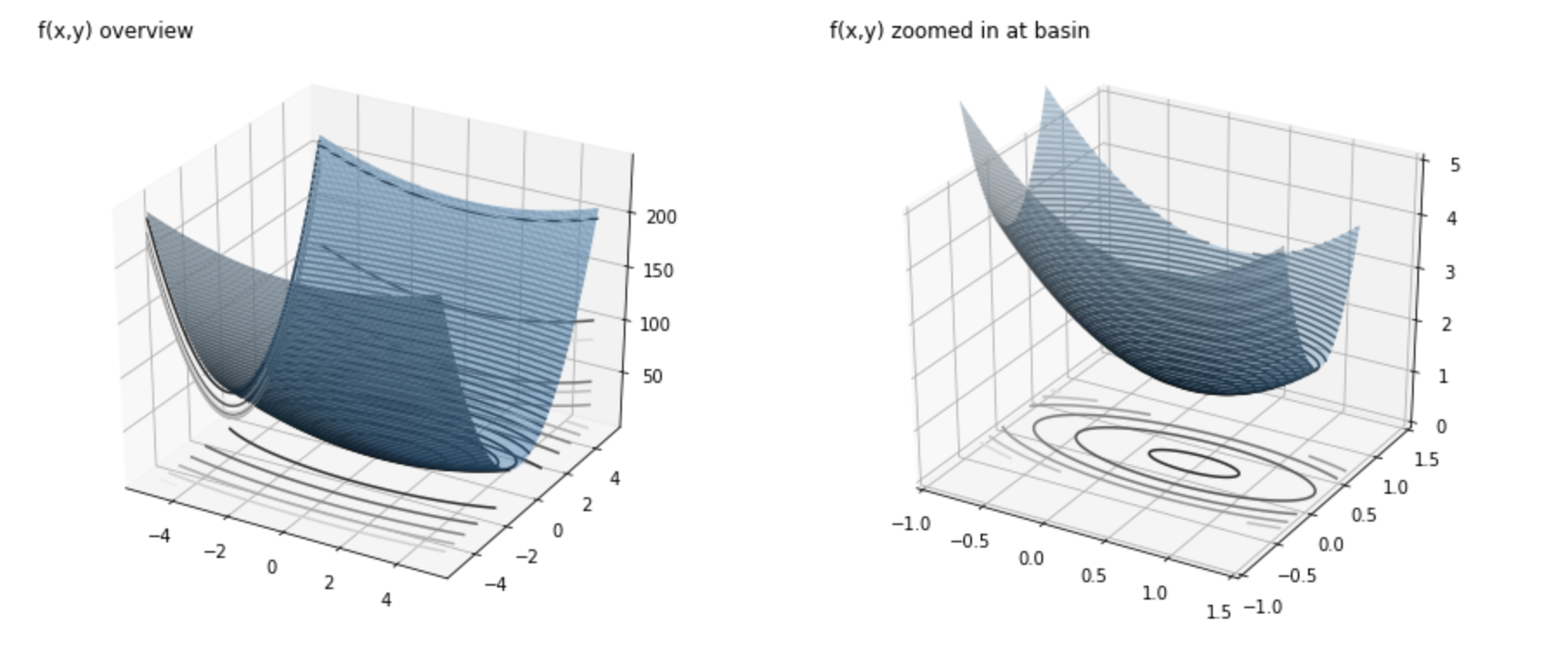
Steepest descent using optimal step size:
def f(x, y):
return (x+1)**2 + 8*y**2 - 3*x - 3*y + 1
# Initiate Q and grad_f defined by given function
def Q():
return np.array([[2, 0], [0, 16]])
def grad_f(x_k, y_k):
# returns gradient of f at xv_k
return np.array([[2 * x_k - 1], [16 * y_k - 1]])
# calculates dot products
def dot_prod(a, b):
# computes the dot product of vectors a and b
if len(a) != len(b):
print("DOT PROD NOT DEFINED")
else:
prod = 0
for i in range(len(a)):
temp = a[i] * b[i]
prod = prod + temp
return prod
# steepest descent algorithm
def alpha(x_k, y_k):
return dot_prod(grad_f(x_k, y_k), grad_f(x_k, y_k)) / dot_prod(grad_f(x_k, y_k), np.matmul(Q(), grad_f(x_k, y_k)))
def xv_k_1(x_k, y_k):
a_k = alpha(x_k, y_k)
grad_f_x_k, grad_f_y_k = grad_f(x_k, y_k).T[0]
x_k_1 = x_k - a_k * grad_f_x_k
y_k_1 = y_k - a_k * grad_f_y_k
return np.array([x_k_1, y_k_1])
def steepest_desc(x_0, y_0):
# arrays to store descent progress at each k
X, Y = [x_0], [y_0]
epsilon = 10 ** (-6)
for k in range(10 ** 4): # i want to stop after at most k = 10**4-1
if np.linalg.norm(grad_f(X[len(X) - 1], Y[len(Y) - 1])) >= epsilon:
next_X, next_Y = xv_k_1(X[len(X) - 1], Y[len(Y) - 1]).T[0]
X.append(next_X)
Y.append(next_Y)
else:
break
return [len(X), X, Y]
# investigate convergence speed
min_point = np.array([0.5, 1 / 16])
starting_dist_from_min = []
x_0_list = []
y_0_list = []
steps_list = []
for x_0 in range(-5, 6):
for y_0 in range(-5, 6):
start = np.array([x_0, y_0])
steps = steepest_desc(x_0, y_0)[0]
starting_dist_from_min.append(np.linalg.norm(start - min_point))
steps_list.append(steps)
x_0_list.append(x_0)
y_0_list.append(y_0)
print("steps =", steps, " start: (", x_0, y_0, ")")